
Vulnerability management is a continuous and proactive process that identifies, assesses, prioritizes, and mitigates vulnerabilities to keep your computer systems, networks, and applications safe from cyberattacks and data breaches.
When vulnerabilities go unresolved, cybercriminals can exploit them to breach critical systems, steal sensitive data, and disrupt business operations. These situations highlight the importance of robust vulnerability management practices.
The main goal is to lower risk exposure by fixing as many vulnerabilities as possible.
This article dives deep into vulnerability management, explaining:
Let’s face it, headlines about cyberattacks are all too common these days. But the statistics paint an even more alarming picture. According to Hiscox, 41% of small businesses were hit by cyberattacks in 2023, up from 38% in 2022 and almost double the 2021 figure.
The financial impact is just as concerning. US small businesses paid over $16,000 on average in cyber ransoms last year alone. This doesn’t include the cost of downtime, data recovery, or legal consequences post-breach.
The rise in cyberattacks targeting small businesses isn’t a coincidence. Attackers see them as easier targets than larger companies with strong security. Unfortunately, many lack the resources and expertise needed to fight back.
The good news? Vulnerability management is a powerful defense by regularly scanning your systems for weaknesses. You then address these vulnerabilities, staying ahead of potential threats.
Before anything else, let’s first discuss some cybersecurity basics.
These cybersecurity terms are often confused to mean the same. To understand the differences, let’s define vulnerability, threat, and risk.
Think of vulnerabilities as weaknesses, threats as potential attackers, and risk as the combined danger they pose.
Vulnerabilities can stem from various sources, including:
Knowing how your systems can be attacked helps you take proactive measures to fix and strengthen your defenses.
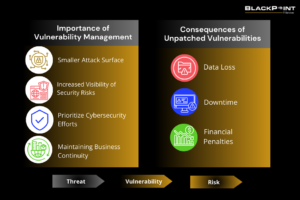
Unpatched vulnerabilities = security gaps. Vulnerability management helps you close these gaps, directly benefiting your business by:
Failing to address vulnerabilities in your computer systems can have severe consequences for your business, such as:
Having established the critical role of vulnerability management, let’s explore the process itself.
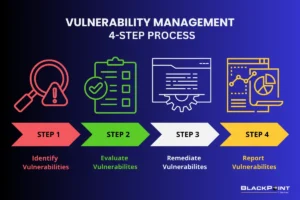
Identifying vulnerabilities is like giving your systems a thorough security checkup. Automated vulnerability scanning tools find potential weaknesses across systems, networks, and applications. They check hardware, software, and network configurations for gaps attackers could exploit. When a vulnerability is detected, the scanner flags it for remediation. The goal is to provide detailed reports that pinpoint vulnerabilities.
Once potential vulnerabilities and misconfigurations are identified, they undergo validation to confirm them as true vulnerabilities. They are then rated according to risk and prioritized based on these risk ratings. This process ensures a focused approach to addressing the most critical security risks.
Vulnerabilities are prioritized based on severity, exploitability, and potential impact:
This means taking corrective actions to address vulnerabilities found in your system. Common techniques include patching software, configuration changes, upgrading hardware, and implementing security controls.
You can choose between full remediation, mitigation, or acceptance of vulnerabilities based on their risk assessment.
Regular vulnerability scans and reports act as ongoing security briefings. They provide valuable insights into your overall security health, emerging threats, and trends in vulnerabilities. This allows your organization to stay proactive in managing cybersecurity risks, track progress, and allocate resources effectively.
It also fosters transparency and accountability by documenting details, remediation progress, and recommendations for IT managers and security officers.
You can establish an effective vulnerability management program by following these four steps—identify, evaluate, remediate, and report. This proactive approach will significantly reduce the risk of cyberattacks and keep your organization safe and secure.
BlackPoint IT offers comprehensive cybersecurity solutions to protect your digital assets and take the security burden off your shoulders.
Here’s what you get with BlackPoint IT:
Ready to be proactive about cybersecurity? Schedule an initial free consultation today and find out how you can ensure protection of your critical business data and assets.